Outcomes of patients undergoing radiation therapy for bladder cancer

Objectives: To review our two institutional experiences regarding the historical referral patterns of bladder cancer patients to receive radiation therapy, characteristics of these referred patients, and their treatment outcomes.
Methods: A retrospective review was performed analyzing patients who underwent radiation therapy for bladder cancer from 2005 to 2015 (n = 69) at two regional referral institutions. The age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index (AACCI) was calculated for each patient. Patients were divided into three groups: definitive concurrent chemoradiation (CCR), aggressive radiation (AR) alone ≥ 50 Gy, or palliative radiation alone (PR) < 50 Gy. Gastrointestinal (GI) and genitourinary (GU) acute toxicities were recorded.
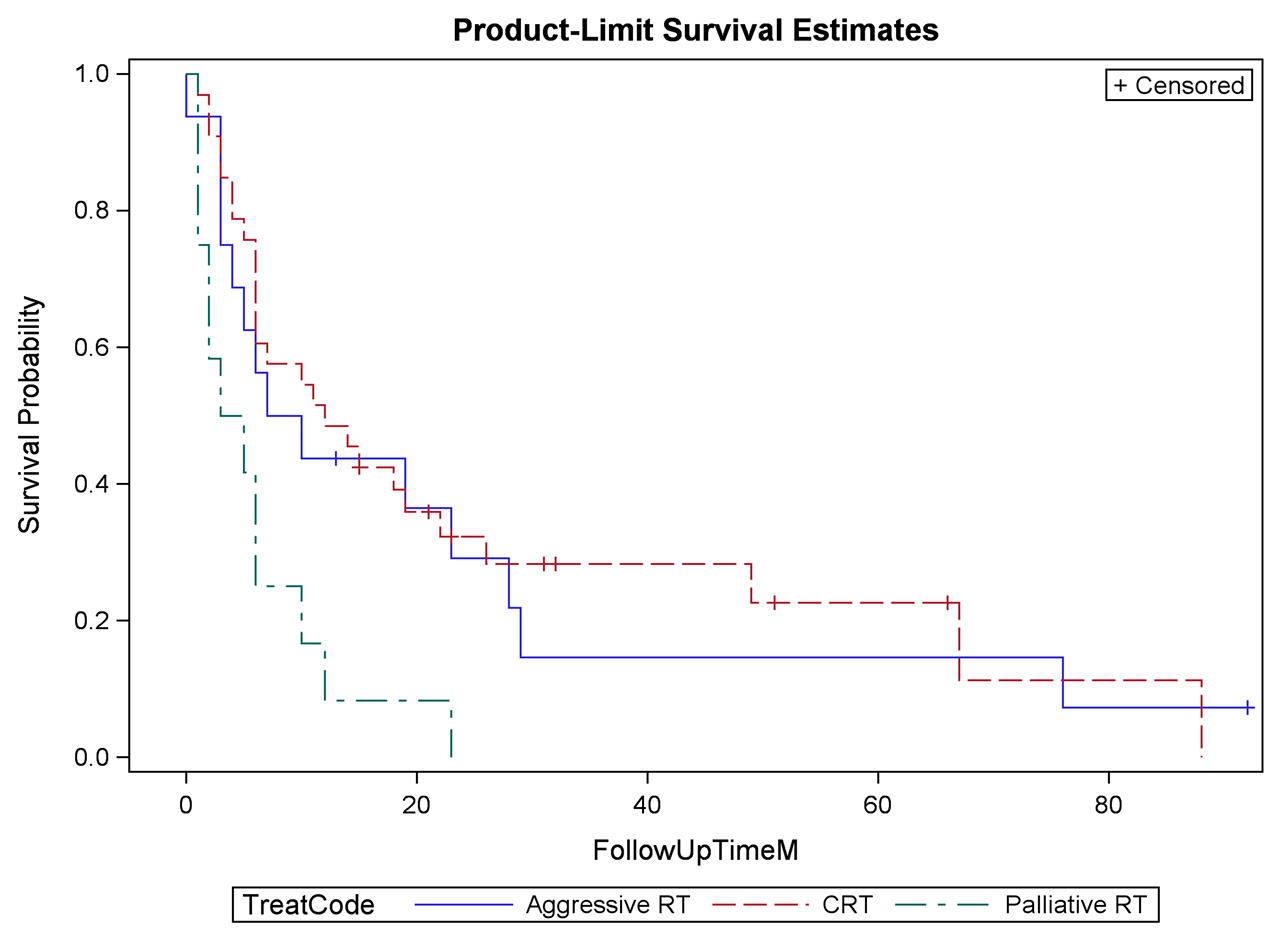
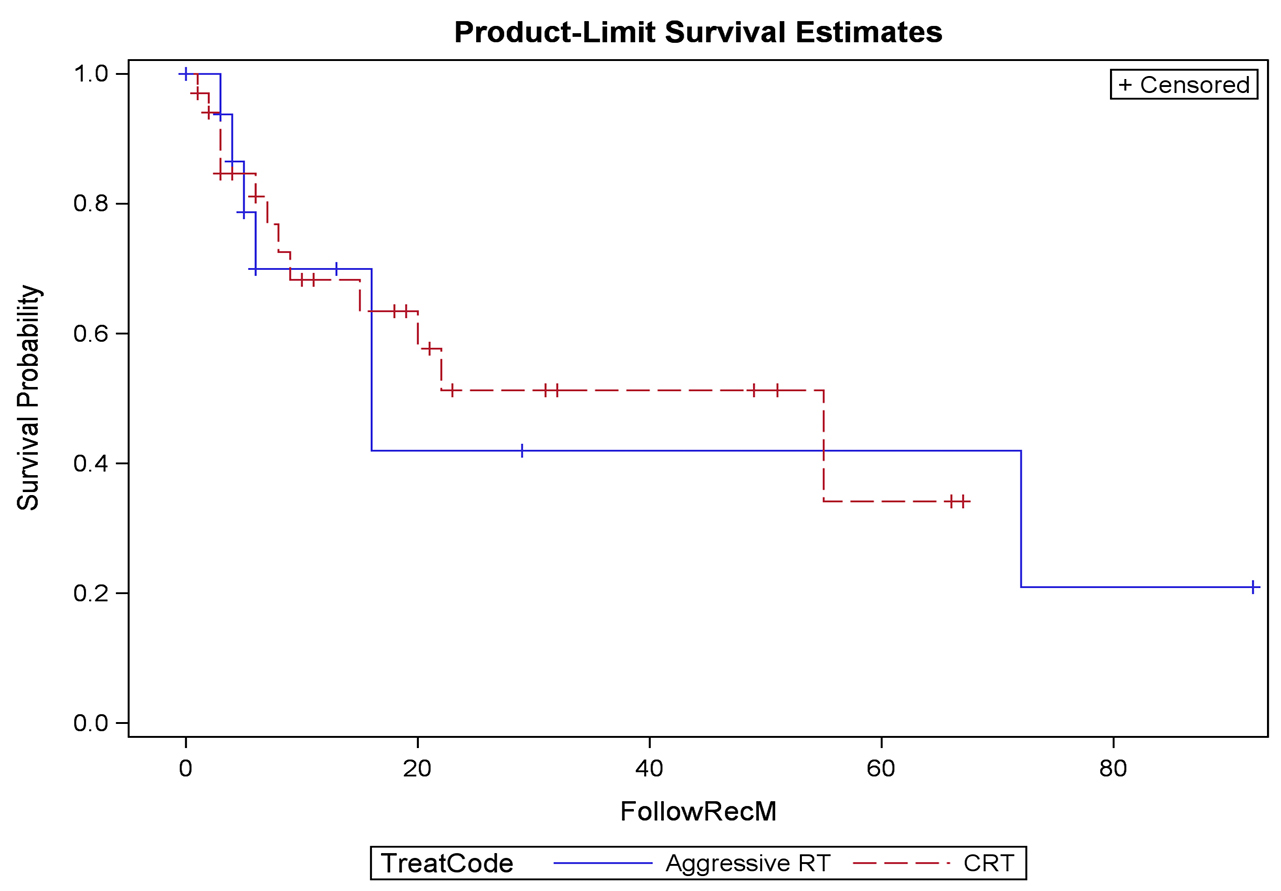
Results: The median overall AACCI score was 7, which correlates to a two-year expected survival of 55% ± 11%. Thirty-five (50.7%) patients received CCR, 19 (27.5%) received AR, and 15 (21.7%) received PR. Patients presented with hematuria (n = 43, 62%), pain (n = 18, 26%), or obstruction (n = 12, 17%). Of symptomatic patients, treatment improved hematuria in 86%, pain in 75%, and obstruction in 42%. Twenty-two recurrences (32%) were identified at follow-up. Local, regional, and distant recurrences developed in 20%, 14%, and 17% of patients who received CCR. There were two grade 3 GU toxicities and one grade 3 GI toxicity; all grade 3 toxicities were in patients receiving CCR.
Conclusions: Bladder preservation is possible with chemoradiation therapy; however, urologists rarely refer patients for consideration of chemoradiation. The limited patients who are referred for radiation generally have limited life expectancy, significant comorbidities, or have advanced disease amenable only to palliation. Palliative radiation improves symptoms with minimal toxicity.
INTRODUCTION
PATIENTS AND METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
| Characteristic | Total patients (N = 69) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 73 (37–98) | |
| Sex, N (%) | ||
| Male | 49 (71) | |
| Female | 20 (29) | |
| Smoking history (%) | ||
| Yes | 50 (72) | |
| No | 17 (25) | |
| Missing data | 2 (3) | |
| Pack years, average (range) | 41.8 (0–175) | |
| AACCI, N (%) | ||
| 3–5 | 12 (17) | |
| 6–7 | 28 (41) | |
| > 7 | 29 (42) | |
| Stage, N (%) | ||
| Stage I | 3 (4) | |
| Stage II | 35 (52) | |
| Stage III | 10 (15) | |
| Stage IV | 19 (28) | |
| T stage, N (%) | ||
| T1 | 4 (6) | |
| T2 | 43 (67) | |
| T3 | 10 (16) | |
| T4 | 7 (11) | |
| Regional nodal status, N (%) | ||
| Positive | 12 (18) | |
| Negative | 53 (82) | |
| Distant metastasis, N (%) | ||
| Positive | 15 (22) | |
| Negative | 52 (78) | |
| Histology, N (%) | ||
| Urothelial | 53 (80) | |
| Squamous | 5 (8) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 3 (5) | |
| Neuroendocrine | 1 (2) | |
| Mixed | 4 (6) | |
| Hydronephrosis, N (%) | ||
| Present | 29 (44) | |
| Negative | 37 (56) | |
| Treatment | ||
| Definitive (CCR) | 35 (51) | |
| Aggressive radiation | 19 (28) | |
| Palliative radiation | 15 (22) |
| Weight | Comorbid condition |
|---|---|
| 1 | Myocardial infarction |
| Congestive heart failure | |
| Peripheral vascular disease | |
| Cerebral vascular disease | |
| Dementia | |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | |
| Connective tissue disorder | |
| Ulcer disease | |
| Mild liver disease | |
| Diabetes | |
| 2 | Hemiplegia |
| Moderate/severe renal disease | |
| Diabetes with endo organ damage | |
| Any tumor | |
| Leukemia | |
| Lymphoma | |
| 3 | Moderate/severe liver disease |
| 6 | Metastatic solid tumor |
| AIDS | |
| 1 | For each decade over the age 40 years |
| Total score | 2-year estimated expected survival |
|---|---|
| 3–5 | 80%–95% |
| 6–7 | 55% |
| > 7 | < 35% |
-
-
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68: 7-30. doi: https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Konety BR, Allareddy V, Herr H (2006) Complications after radical cystectomy: analysis of population-based data. Urology 68: 58-64. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2006.01.051. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Donat SM, Shabsigh A, Savage C, Cronin AM, Bochner BH, et al. (2008) Potential impact of postoperative early complications on the timing of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients undergoing radical cystectomy: a high-volume tertiary cancer center experience. Eur Urol 55: 177-185. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2008.07.018. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Huddart RA, Hall E, Lewis R, Birtle A (2010) Life and death of spare (selective bladder preservation against radical excision): reflections on why the spare trial closed. BJU Int 106: 753-755. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09537.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
James ND, Hussain SA, Hall E, Jenkins P, Tremlett J, et al. (2012) Radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 366: 1477-1488. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1106106. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Mak RH, Hunt D, Shipley WU, Efstathiou JA, Tester WJ, et al. (2014) Long-term outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after selective bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy: a pooled analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group protocols 8802, 8903, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233. J Clin Oncol 32: 3801-3809. doi: https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.57.5548. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Vashistha V, Wang H, Mazzone A, Liss MA, Svatek RS, et al. (2016) Radical Cystectomy Compared to Combined Modality Treatment for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 97: 1002-1020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.11.056. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Duchesne GM, Bolger JJ, Griffiths GO, Trevor Roberts J, Graham JD, et al. (2000) A randomized trial of hypofractionated schedules of palliative radiotherapy in the management of bladder carcinoma: results of medical research council trial BA09. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47: 379-388. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00430-2. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
McLaren DB, Morrey D, Mason MD (1997) Hypofractionated radiotherapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer in the elderly. Radiother Oncol 43: 171-174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lacarrière E, Smaali C, Benyoucef A, Pfister C, Grise P (2013) The efficacy of hemostatic radiotherapy for bladder cancer-related hematuria in patients unfit for surgery. Int Braz J Urol 39: 808-816. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.06.06. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Gray PJ, Fedewa SA, Shipley WU, Efstathiou JA, Lin CC, et al. (2013) Use of potentially curative therapies for muscle-invasive bladder cancer in the United States: results from the National Cancer Data Base. European Urology 63: 823-829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.015. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Haque W, Verma V, Butler EB, Teh BS (2017) National practice patterns and outcomes for T4b urothelial cancer of the bladder. Clin Genitourin Cancer doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2017.08.013. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Beddhu S, Bruns FJ, Saul M, Seddon P, Zeidel ML (2000) A simple comorbidity scale predicts clinical outcomes and costs in dialysis patients. Am J Med 108: 609-613. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00371-5. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Koppie TM, Serio AM, Vickers AJ, Vora K, Dalbagni G, et al. (2008) Age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity score is associated with treatment decisions and clinical outcomes for patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Cancer 112: 2384-2392. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23462. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
National Institutes of Health. National Cancer Institute (2018) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). Cited on May 24, 2018. Available from: https://ctep.cancer.gov. [Google Scholar]
-
Centers for Disease Control (2018) Smoking & Tobacco Use. Cited on May 24, 2018. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco.
-
National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (2018) SEER Cancer Stat Facts. Cited on May 24, 2018. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts. Cited on May 24: [Google Scholar]
-
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2018) Evidence-Based Cancer Guidelines. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/.
-
Shipley WU, Kaufman DS, Zehr E, Heney NM, Lane SC, et al. (2002) Selective bladder preservation by combined modality protocol treatment: long-term outcomes of 190 patients with invasive bladder cancer. Urology 60: 62-67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Gestaut MM, Swanson GP (2016) Long term clinical toxicity of radiation therapy in prostate cancer patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 22: 77-82. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2016.10.005. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Efstathiou JA, Bae K, Shipley WU, Kaufman DS, Hagan MP, et al. (2009) Late pelvic toxicity after bladder-sparing therapy in patients with invasive bladder cancer: RTOG 89-03, 95-06, 97-06, 99-06. J Clin Oncol 27: 4055-4061. doi: https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.19.5776. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Zaghloul MS (2012) Bladder cancer and schistosomiasis. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 24: 151-159. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnci.2012.08.002. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sabaa MA, El-Gamal OM, Abo-Elenen M, Khanam A (2008) Combined modality treatment with bladder preservation for muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urol Oncol 28: 14-20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.07.005. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Williams SB, Shan Y, Jazzar U, Mehta HB, Baillargeon JG, et al. (2018) Comparing Survival Outcomes and Costs Associated With Radical Cystectomy and Trimodal Therapy for Older Adults With Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. JAMA Surg 153: 881-889. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1680. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chang SS, Bochner BH, Chou R, Dreicer R, Kamat AM, et al. (2017) Treatment of Non-Metastatic Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO Guideline. J Urol 198: 552-559. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.04.086. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-

