Purinergic P2X7 receptors as therapeutic targets in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome; key role of ATP signaling in inflammation

Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is a chronic lower urinary tract condition. Patients with IC/BPS suffer from debilitating pain and urinary urgency. The underlying etiology of IC/BPS is unknown and as such current treatments are mostly symptomatic with no real cure. Many theories have been proposed to describe the etiology of IC/BPS, but this review focuses on the role of inflammation. In IC/BPS patients, the permeability of the urothelium barrier is compromised and inflammatory cells infiltrate the bladder wall. There are increased levels of many inflammatory mediators in patients with IC/BPS and symptoms such as pain and urgency that have been associated with the degree of inflammation. Recent evidence has highlighted the role of purinergic receptors, specifically the P2X7 receptor, in the process of inflammation. The results from studies in animals including cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis strongly support the role of P2X7 receptors in inflammation. Furthermore, the deletion of the P2X7 receptor or antagonism of this receptor significantly reduces inflammatory mediator release from the bladder and improves symptoms. Research results from IC/BPS patients and animal models of IC/BPS strongly support the crucial role of inflammation in the pathophysiology of this painful disease. Purinergic signaling and purinergic receptors, especially the P2X7 receptor, play an undisputed role in inflammation. Purinergic receptor antagonists show positive results in treating different symptoms of IC/BPS.
INTRODUCTION
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/BLADDER PAIN SYNDROME
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
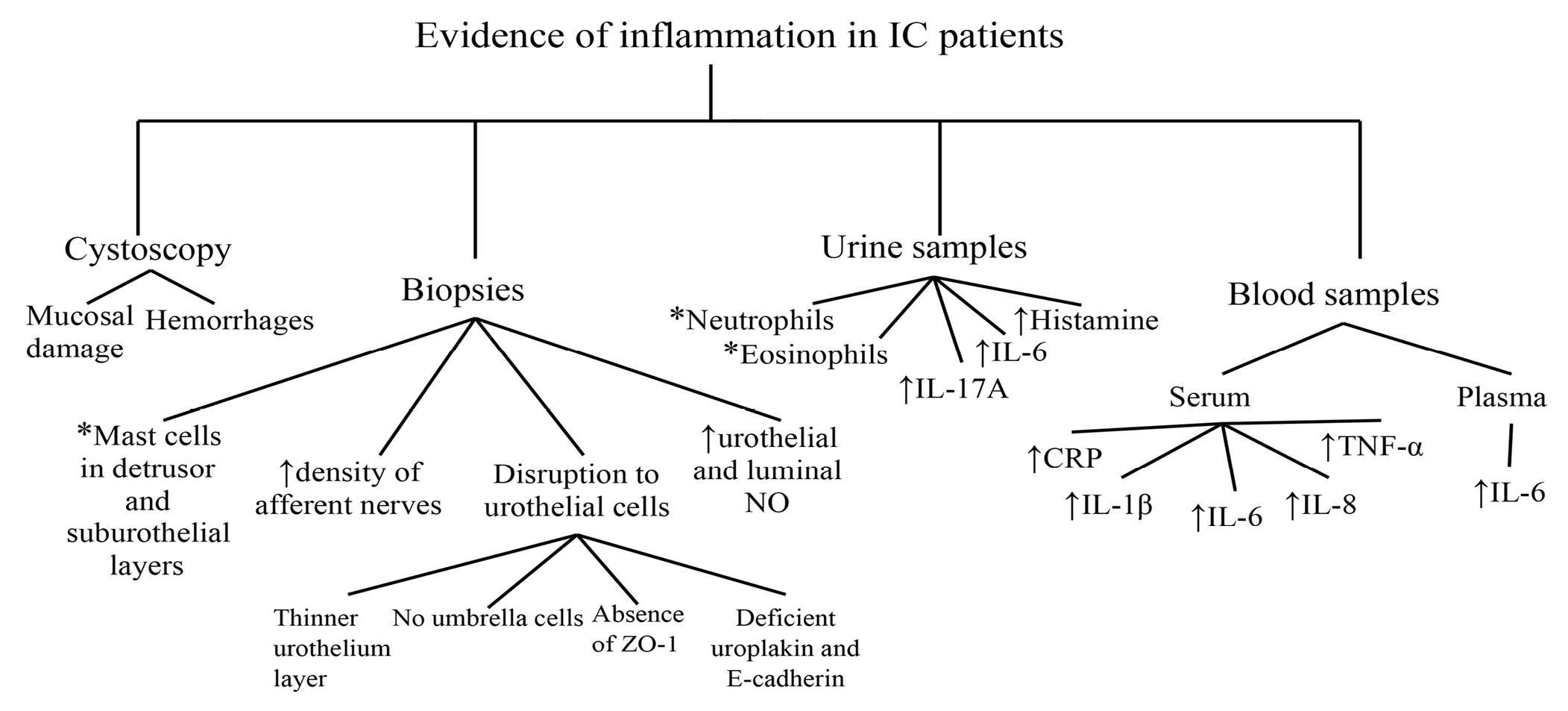
CLINICAL EVIDENCE OF INFLAMMATION IN IC/BPS
Observations from cystoscopy and biopsy samples from IC/BPS patients
Urothelial changes
Increased inflammatory mediators
Role of sensory nerve fibers
ATP AS A SIGNALING MOLECULE FOR BLADDER PAIN AND URGENCY
P2X7 PURINERGIC RECEPTOR—A MODULATOR OF INFLAMMATION
CONCLUSION
-
-
Cox A, Golda N, Nadeau G, Curtis Nickel J, Carr L, et al. (2016) CUA guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Can Urol Assoc J 10: E136-E155. doi: https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.3786. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Warren JW, Meyer WA, Greenberg P, Horne L, Diggs C, et al. (2006) Using the International Continence Society's definition of painful bladder syndrome. Urology 67: 1138-1143. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2006.01.086. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
van de Merwe, P. (Joop) , Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, Bouchelouche K, Cervigni M, et al. (2007) Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol 53: 60-67. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.019. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, et al. (2002) The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187: 116-126. doi: https://doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.125704. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Horn T, Holm NR, Hald T (1998) Interstitial cystitis. Ultrastructural observations on detrusor smooth muscle cells. APMIS 106: 909-916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Bogart LM, Berry SH, Clemens JQ (2007) Symptoms of interstitial cystitis, painful bladder syndrome and similar diseases in women: a systematic review. J Urol 177: 450-456. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2006.09.032. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Foster HE Jr, Hanno PM, Nickel JC, Payne CK, Mayer RD, et al. (2010) Effect of amitriptyline on symptoms in treatment naive patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol 183: 1853-18588. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.106. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Han E, Nguyen L, Sirls L, Peters K (2018) Current best practice management of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Ther Adv Urol 10: 197-211. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287218761574. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
van Ophoven A, Pokupic S, Heinecke A, Hertle L (2004) A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind study of amitriptyline for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. J Urol 172: 533-536. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000132388.54703.4d. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, et al. (2011) AUA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol 185: 2162-2170. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.064. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sairanen J, Tammela TL, Leppilahti M, Multanen M, Paananen I, et al. (2005) Cyclosporine A and pentosan polysulfate sodium for the treatment of interstitial cystitis: a randomized comparative study. J Urol 174: 2235-2238. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000181808.45786.84. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Forrest JB, Payne CK, Erickson DR (2012) Cyclosporine A for refractory interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: experience of 3 tertiary centers. J Urol 188: 1186-1191. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.023. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Theoharides TC, Sant GR (1997) Hydroxyzine therapy for interstitial cystitis. Urology 49: 108-110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Perez-Marrero R, Emerson LE, Feltis JT (1988) A controlled study of dimethyl sulfoxide in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 140: 36-39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Parsons CL, Housley T, Schmidt JD, Lebow D (1994) Treatment of interstitial cystitis with intravesical heparin. Br J Urol 73: 504-507. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.1994.tb07634.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Parsons CL, Zupkas P, Proctor J, Koziol J, Franklin A, et al. (2012) Alkalinized lidocaine and heparin provide immediate relief of pain and urgency in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Sex Med 9: 207-212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02542.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Stav K, Beberashvili I, Lindner A, Leibovici D (2012) Predictors of response to intravesical dimethyl-sulfoxide cocktail in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology 80: 61-65. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.03.030. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Kuo H (2013) Repeated onabotulinumtoxin-a injections provide better results than single injection in treatment of painful bladder syndrome. Pain Physician 16: E15-23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Giannantoni A, Costantini E, Di Stasi SM, Tascini MC, Bini V, et al. (2006) Botulinum A toxin intravesical injections in the treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a pilot study. Eur Urol 49: 704-709. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.002. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Giannantoni A, Mearini E, Del Zingaro M, Proietti S, Porena M (2010) Two-year efficacy and safety of botulinum a toxin intravesical injections in patients affected by refractory painful bladder syndrome. Curr Drug Deliv 7: 1-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Pinto R, Lopes T, Frias B, Silva A, Silva JA, et al. (2010) Trigonal injection of botulinum toxin A in patients with refractory bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Eur Urol 58: 360-365. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.02.031. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Barua JM, Arance I, Angulo JC, Riedl CR (2016) A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 27: 1137-1147. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-015-2890-7. [View Article] [PubMed]
-
Sant GR, Propert KJ, Hanno PM, Burks D, Culkin D, et al. (2003) A pilot clinical trial of oral pentosan polysulfate and oral hydroxyzine in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 170: 810-815. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000083020.06212.3d. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Bade JJ, Laseur M, Nieuwenburg A, van der Weele LT, Mensink HJ (1997) A placebo-controlled study of intravesical pentosanpolysulphate for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 79: 168-171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410X.1997.03384.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sairanen J, Leppilahti M, Tammela TL, Paananen I, Aaltomaa S, et al. (2009) Evaluation of health-related quality of life in patients with painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis and the impact of four treatments on it. Scand J Urol Nephrol 43: 212-219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00365590802671031. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Tutolo M, Ammirati E, Castagna G, Klockaerts K, Plancke H, et al. (2017) A prospective randomized controlled multicentre trial comparing intravesical DMSO and chondroitin sulphate 2% for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Braz J Urol 43:134-141. Epub PubMed Central PMCID: 134-141. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-5538.Ibju.2016.0302. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Johansson SL, Fall M (1990) Clinical features and spectrum of light microscopic changes in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 143: 1118-1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Logadottir Y, Fall M, Kåbjörn-Gustafsson C, Peeker R (2012) Clinical characteristics differ considerably between phenotypes of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 46: 365-370. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/00365599.2012.689008. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Tomoe H (2015) In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?. Transl Androl Urol 4: 600-604. doi: https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.09.01. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lee JE, Yi BH, Lee HK, Lee MH, Kim YH (2015) Correlation of cystoscopically confirmed periureterally located hunner lesion with vesicoureteral reflux: preliminary study in patients with interstitial cystitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204: W457-W460. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.14.13108. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Grover S, Srivastava A, Lee R, Tewari AK, Te AE (2011) Role of inflammation in bladder function and interstitial cystitis. Ther Adv Urol 3: 19-33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287211398255. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Liu HT, Jiang YH, Kuo HC (2015) Alteration of urothelial inflammation, apoptosis, and junction protein in patients with various bladder conditions and storage bladder symptoms suggest common pathway involved in underlying pathophysiology. Low Urin Tract Symptoms 7: 102-107. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/luts.12062. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Eldrup J, Thorup J, Nielsen SL, Hald T, Hainau B (1983) Permeability and ultrastructure of human bladder epithelium. Br J Urol 55: 488-492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Said JW, Van de Velde R, Gillespie L (1989) Immunopathology of interstitial cystitis. Mod Pathol 2: 593-602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Parsons CL, Lilly JD, Stein P (1991) Epithelial dysfunction in nonbacterial cystitis (interstitial cystitis). J Urol 145: 732-735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Liu BL, Yang F, Zhan HL, Feng ZY, Zhang ZG, et al. (2014) Increased severity of inflammation correlates with elevated expression of TRPV1 nerve fibers and nerve growth factor on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urol Int 92: 202-208. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000355175. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Pang X, Cotreau-Bibbo MM, Sant GR, Theoharides TC (1995) Bladder mast cell expression of high affinity oestrogen receptors in patients with interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 75: 154-161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Pang X, Marchand J, Sant GR, Kream RM, Theoharides TC (1995) Increased number of substance P positive nerve fibres in interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 75: 744-750. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.1995.tb07384.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Yamada T, Murayama T, Mita H, Akiyama K (2000) Subtypes of bladder mast cells in interstitial cystitis. Int J Urol 7: 292-297. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1442-2042.2000.00197.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Slobodov G, Feloney M, Gran C, Kyker KD, Hurst RE, et al. (2004) Abnormal expression of molecular markers for bladder impermeability and differentiation in the urothelium of patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 171: 1554-1558. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000118938.09119.a5. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Graham E, Chai TC (2006) Dysfunction of bladder urothelium and bladder urothelial cells in interstitial cystitis. Curr Urol Rep 7: 440-446. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-006-0051-8. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Montalbetti N, Rued AC, Clayton DR, Ruiz WG, Bastacky SI, et al. (2015) Increased urothelial paracellular transport promotes cystitis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309: F1070-F1081. Epub PubMed Central PMCID: doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00200.2015. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sasisekharan R, Raman R, Prabhakar V (2006) Glycomics approach to structure-function relationships of glycosaminoglycans. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8: 181-231. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095745. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Hurst RE, Roy JB, Min KW, Veltri RW, Marley G, et al. (1996) A deficit of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on the bladder uroepithelium in interstitial cystitis. Urology 48: 817-821. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(96)00322-6. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Hurst RE (2003) A deficit of proteoglycans on the bladder uroepithelium in interstitial cystitis. Eur Urol Suppl 2: 10-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1569-9056(03)00033-2. [View Article]
-
Lavelle JP, Negrete HO, Poland PA, Kinlough CL, Meyers SD, et al. (1997) Low permeabilities of MDCK cell monolayers: a model barrier epithelium. Am J Physiol 273: doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.1997.273.1.F67. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Huygens A, Crnolatac I, Maes J, Cleynenbreugel B, Van Poppel H, et al. (2007) Influence of the glycosaminoglycan layer on the permeation of hypericin in rat bladders in vivo. BJU international 100: 1176-1181. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07167.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lewis SA (2000) Everything you wanted to know about the bladder epithelium but were afraid to ask. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278: doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2000.278.6.F867. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lewis SA, Berg JR, Kleine TJ (1995) Modulation of epithelial permeability by extracellular macromolecules. Physiol Rev 75: 561-589. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1995.75.3.561. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Cvach K, Rosamilia A (2015) Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Transl Androl Urol 4: 629-637. doi: https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.10.07. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Katnik-Prastowska I, Lis J, Matejuk A (2014) Glycosylation of uroplakins. Implications for bladder physiopathology. Glycoconj J 31: 623-636. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-014-9564-4. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Aldenborg F, Fall M, Enerbäck L (1986) Proliferation and transepithelial migration of mucosal mast cells in interstitial cystitis. Immunology 58: 411-416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Logadottir Y, Delbro D, Fall M, Gjertsson I, Jirholt P, et al. (2014) Cytokine expression in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis ESSIC type 3C. J Urol 192: 1564-1568. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.04.099. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Dodd LG, Tello J (1998) Cytologic examination of urine from patients with interstitial cystitis. Acta Cytol 42: 923-927. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000331969. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P (2013) Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 13: 159-175. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3399. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Fulkerson PC, Rothenberg ME (2013) Targeting eosinophils in allergy, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12: 117-129. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3838. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Fall M, Johansson SL, Aldenborg F (1987) Chronic interstitial cystitis: a heterogeneous syndrome. J Urol 137: 35-38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Zhong CJ, Wang K, Zhang L, Yang CQ, Zhang K, et al. (2015) Mast cell activation is involved in stress-induced epithelial barrier dysfunction in the esophagus. J Dig Dis 16: 186-196. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-2980.12226. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Peeker R, Enerback L, Fall M, Recruitment AF (2000) Recruitment, distribution and phenotypes of mast cells in interstitial cystitis. J Urol 163: 1009-1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Hofmeister MA, He F, Ratliff TL, Mahoney T, Becich MJ (1997) Mast cells and nerve fibers in interstitial cystitis (IC): An algorithm for histologic diagnosis via quantitative image analysis and morphometry (QIAM). Urology 49: 41-47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-4295(99)80330-6. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sant GR, Theoharides TC (1994) The role of the mast cell in interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am 21: 41-53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Holm-Bentzen M, Søndergaard I, Hald T (1987) Urinary excretion of a metabolite of histamine (1,4-methyl-imidazole-acetic-acid) in painful bladder disease. Br J Urol 59: 230-233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lamale LM, Lutgendorf SK, Zimmerman MB, Kreder KJ (2006) Interleukin-6, histamine, and methylhistamine as diagnostic markers for interstitial cystitis. Urology 68: 702-706. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2006.04.033. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Koskela LR, Thiel T, Ehren I, De Verdier PJ, Wiklund NP (2008) Localization and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in biopsies from patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 180: 737-741. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.03.184. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sharma JN, Al-Omran A, Parvathy SS (2007) Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 15: 252-259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-007-0013-x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Offiah I, Didangelos A, Dawes J, Cartwright R, Khullar V, et al. (2016) The expression of inflammatory mediators in bladder pain syndrome. Eur Urol 70: 283-290. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.058. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Jin W, Dong C (2013) IL-17 cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Emerg Microbes Infect 2: e60. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2013.58. [View Article]
-
Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Nagai T, Kadoki M, Nambu A, et al. (2009) Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 30: 108-19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.009. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T (2014) IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6: a016295. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016295. [View Article] [PubMed]
-
Schrepf A, O'Donnell M, Luo Y, Bradley CS, Kreder K, et al. (2014) Inflammation and inflammatory control in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Associations with painful symptoms. Pain 155: 1755-1761. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.05.029. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Jiang YH, Peng CH, Liu HT, Kuo HC (2013) Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, C-reactive protein and nerve growth factor expressions in serum of patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. PLoS One 8: e76779. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076779. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sakthivel SK, Singh UP, Singh S, Taub DD, Novakovic KR, et al. (2008) CXCL10 blockade protects mice from cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J Immune Based Ther Vaccines 6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-8518-6-6. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Martins JP, Silva RB, Coutinho-Silva R, Takiya CM, Battastini AM, et al. (2011) The role of P2X7 purinergic receptors in inflammatory and nociceptive changes accompanying cyclophosphamide-induced haemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Br J Pharmacol 165: 183-196. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01535.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Christmas TJ, Rode J, Chapple CR, Milroy EJ, Turner-Warwick RT (1990) Nerve fibre proliferation in interstitial cystitis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 416: 447-451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01605152. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lundeberg T, Liedberg H, Nordling L, Theodorsson E, Owzarski A, et al. (1993) Interstitial cystitis: correlation with nerve fibres, mast cells and histamine. Br J Urol 71: 427-429. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.1993.tb15986.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Kim SW, Im YJ, Choi HC, Kang HJ, Kim JY, et al. (2014) Urinary nerve growth factor correlates with the severity of urgency and pain. Int Urogynecol J 25: 1561-1567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-014-2424-8. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Yaraee R, Ebtekar M, Ahmadiani A, Sabahi F (2003) Neuropeptides (SP and CGRP) augment pro-inflammatory cytokine production in HSV-infected macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 3: 1883-1887. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1567-5769(03)00201-7. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Azzolina A, Bongiovanni A, Lampiasi N (2003) Substance P induces TNF-alpha and IL-6 production through NF kappa B in peritoneal mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1643: 75-83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ang SF, Moochhala SM, MacAry PA, Bhatia M (2011) Hydrogen sulfide and neurogenic inflammation in polymicrobial sepsis: involvement of substance P and ERK-NF-kappaB signaling. PLoS One 6: e24535. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024535. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Bhatia M, Zhi L, Zhang H, Ng S, Moore PK (2006) Role of substance P in hydrogen sulfide-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291: doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00053.2006. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Hegde A, Tamizhselvi R, Manikandan J, Melendez AJ, Moochhala SM, et al. (2010) Substance P in polymicrobial sepsis: molecular fingerprint of lung injury in preprotachykinin-A-/- mice. Mol Med 16: 188-198. doi: https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2009.00166. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sio SWS, Ang SF, Lu J, Moochhala S, Bhatia M (2010) Substance P upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E metabolite by activating ERK1/2 and NF-kappaB in a mouse model of burn-induced remote acute lung injury. J Immunol 185: 6265-6276. doi: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1001739. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sio SW, Puthia MK, Lu J, Moochhala S, Bhatia M (2008) The neuropeptide substance P is a critical mediator of burn-induced acute lung injury. J immunol 180: 8333-8341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sipos G, Sipos P, Altdorfer K, Pongor E, Feher E (2008) Correlation and immunolocalization of substance P nerve fibers and activated immune cells in human chronic gastritis. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 291: 1140-1148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.20737. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Burnstock G (1972) Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev 24: 509-581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Kitta T, Chancellor MB, de Groat WC, Kuno S, Nonomura K, et al. (2013) Roles of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in the control of micturition in rats. Neurourol Urodyn 33: 1259-1265. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22487. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Silva I, Costa AF, Moreira S, Ferreirinha F, Magalhaes-Cardoso MT, et al. (2017) Inhibition of cholinergic neurotransmission by beta3-adrenoceptors depends on adenosine release and A1-receptor activation in human and rat urinary bladders. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 313: F388-F403. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00392.2016. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Pakzad M, Ikeda Y, McCarthy C, Kitney DG, Jabr RI, et al. (2016) Contractile effects and receptor analysis of adenosine-receptors in human detrusor muscle from stable and neuropathic bladders. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 389: 921-929. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1255-1. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Searl TJ, Dynda DI, Alanee SR, El-Zawahry AM, McVary KT, et al. (2015) A1 Adenosine receptor-mediated inhibition of parasympathetic neuromuscular transmission in human and murine urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 356: 116-122. doi: https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.228882. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Burnstock G (2007) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64: 1471-1483. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-6497-0. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chen X, Gebhart GF (2010) Differential purinergic signaling in bladder sensory neurons of naïve and bladder-inflamed mice. Pain 148: 462-472. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2009.12.006. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lee HY, Bardini M, Burnstock G (2000) Distribution of P2X receptors in the urinary bladder and the ureter of the rat. J Urol 163: 2002-2007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Vial C, Evans RJ (2000) P2X receptor expression in mouse urinary bladder and the requirement of P2X(1) receptors for functional P2X receptor responses in the mouse urinary bladder smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 131: 1489-1495. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703720. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Menzies J, Paul A, Kennedy C (2003) P2X7 subunit-like immunoreactivity in the nucleus of visceral smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig. Auton Neurosci 106: 103-109. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1566-0702(03)00078-X. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Svennersten K, Hallen-Grufman K, de Verdier PJ, Wiklund NP, Poljakovic M (2015) Localization of P2X receptor subtypes 2, 3 and 7 in human urinary bladder. BMC Urol 15: 81. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-015-0075-9. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Shabir S, Cross W, Kirkwood LA, Pearson JF, Appleby PA, et al. (2013) Functional expression of purinergic P2 receptors and transient receptor potential channels by the human urothelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305: F396-460. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00127.2013. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Tempest HV, Dixon AK, Turner WH, Elneil S, Sellers LA, et al. (2004) P2X and P2X receptor expression in human bladder urothelium and changes in interstitial cystitis. BJU Int 93: 1344-1348. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.04858.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chua WC, Liu L, Mansfield KJ, Vaux KJ, Moore KH, et al. (2007) Age-related changes of P2X(1) receptor mRNA in the bladder detrusor from men with and without bladder outlet obstruction. Exp Gerontol 42: 686-692. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2007.02.003. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Vlaskovska M, Kasakov L, Rong W, Bodin P, Bardini M, et al. (2001) P2X3 knock-out mice reveal a major sensory role for urothelially released ATP. J Neurosci 21: 5670-5677. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05670.2001. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Birder LA, Ruan HZ, Chopra B, Xiang Z, Barrick S, et al. (2004) Alterations in P2X and P2Y purinergic receptor expression in urinary bladder from normal cats and cats with interstitial cystitis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F1084-1091. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00118.2004. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chopra B, Gever J, Barrick SR, Hanna-Mitchell AT, Beckel JM, et al. (2008) Expression and function of rat urothelial P2Y receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294: F821-829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00321.2006. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Carneiro I, Timoteo MA, Silva I, Vieira C, Baldaia C, et al. (2014) Activation of P2Y6 receptors increases the voiding frequency in anaesthetized rats by releasing ATP from the bladder urothelium. Br J Pharmacol 171: 3404-3419. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12711. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Timoteo MA, Carneiro I, Silva I, Noronha-Matos JB, Ferreirinha F, et al. (2014) ATP released via pannexin-1 hemichannels mediates bladder overactivity triggered by urothelial P2Y6 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 87: 371-379. Epub 2013/11/26. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.11.007 87: 371-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.11.007. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sui GP, Wu C, Fry CH (2006) Characterization of the purinergic receptor subtype on guinea-pig suburothelial myofibroblasts. BJU Int 97: 1327-1331. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06200.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Collins VM, Daly DM, Liaskos M, McKay NG, Sellers D, et al. (2013) OnabotulinumtoxinA significantly attenuates bladder afferent nerve firing and inhibits ATP release from the urothelium. BJU Int 112: 1018-1026. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12266. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Cockayne DA, Hamilton SG, Zhu QM, Dunn PM, Zhong Y, et al. (2000) Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice. Nature 407: 1011-1015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/35039519. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sun Y, Keay S, De Deyne PG, Chai TC (2001) Augmented stretch activated adenosine triphosphate release from bladder uroepithelial cells in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 166: 1951-1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sun Y, Chai TC (2005) Augmented extracellular ATP signaling in bladder urothelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290: C27-34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00552.2004. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ferguson DR, Kennedy I, Burton TJ (1998) ATP is released from rabbit urinary bladder epithelial cells by hydrostatic pressure changes--a possible sensory mechanism?. J Physiol 505: 503-511. Epub PubMed Central PMCID: [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sadananda P, Shang F, Liu L, Mansfield KJ, Burcher E (2009) Release of ATP from rat urinary bladder mucosa: role of acid, vanilloids and stretch. Br J Pharmacol 158: 1655-1662. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00431.x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Birder LA, Barrick SR, Roppolo JR, Kanai AJ, de Groat WC, et al. (2003) Feline interstitial cystitis results in mechanical hypersensitivity and altered ATP release from bladder urothelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285: F423-429. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00056.2003. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lazarowski ER (2012) Vesicular and conductive mechanisms of nucleotide release. Purinergic Signal 8: 359-373. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-012-9304-9. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lohman AW, Billaud M, Isakson BE (2012) Mechanisms of ATP release and signalling in the blood vessel wall. Cardiovasc Res 2012 95: 269-280. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvs187. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Burnstock G (2006) Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27: 166-176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2006.01.005. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ho T, Jobling AI, Greferath U, Chuang T, Ramesh A, et al. (2015) Vesicular expression and release of ATP from dopaminergic neurons of the mouse retina and midbrain. Front Cell Neurosci 9: 389. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00389. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sana-Ur-Rehman H, Markus I, Moore KH, Mansfield KJ, Liu L (2017) Expression and localization of pannexin-1 and CALHM1 in porcine bladder and their involvement in modulating ATP release. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 312: R763-R772. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00039.2016. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Locovei S, Scemes E, Qiu F, Spray DC, Dahl G (2007) Pannexin1 is part of the pore forming unit of the P2X(7) receptor death complex. FEBS letters 581: 483-488. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.12.056. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Negoro H, Urban-Maldonado M, Liou LS, Spray DC, Thi MM, et al. (2014) Pannexin 1 channels play essential roles in urothelial mechanotransduction and intercellular signaling. PLoS One 9: e106269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106269. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Sui G, Fry CH, Montgomery B, Roberts M, Wu R, et al. (2013) Purinergic and muscarinic modulation of ATP release from the urothelium and its paracrine actions. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306: F286-298. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00291.2013. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Mansfield KJ, Hughes JR (2014) P2Y receptor modulation of ATP release in the urothelium. Biomed Res Int 2014: 830374-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/830374. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50: 413-492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Yegutkin GG (2008) Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: Important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783: 673-694. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.024. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
McMurray G, Dass N, Brading AF (1998) Purinoceptor subtypes mediating contraction and relaxation of marmoset urinary bladder smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 123: 1579-1586. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0701774. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Fry CH, Young JS, Jabr RI, McCarthy C, Ikeda Y, et al. (2012) Modulation of spontaneous activity in the overactive bladder: the role of P2Y agonists. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302: F1447-1454. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00436.2011. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Birder L, Andersson KE (2013) Urothelial signaling. Physiol Rev 93: 653-680. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2012. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Rong W, Spyer KM, Burnstock G (2002) Activation and sensitisation of low and high threshold afferent fibres mediated by P2X receptors in the mouse urinary bladder. J Physiol 541(Pt 2): 591-600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Zhong Y, Banning AS, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Burnstock G, et al. (2003) Bladder and cutaneous sensory neurons of the rat express different functional p2x receptors. Neuroscience 120: 667-675. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00243-4. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Kumar V, Chapple CR, Surprenant AM, Chess-Williams R (2007) Enhanced adenosine triphosphate release from the urothelium of patients with painful bladder syndrome: a possible pathophysiological explanation. J Urol 178: 1533-1536. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.05.116. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Smith CP, Vemulakonda VM, Kiss S, Boone TB, Somogyi GT (2005) Enhanced ATP release from rat bladder urothelium during chronic bladder inflammation: effect of botulinum toxin A. Neurochem Int 47: 291-297. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.021 47: 291-297. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.021. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Montalbetti N, Rued AC, Taiclet SN, Birder LA, Kullmann FA, et al. (2017) Urothelial tight junction barrier dysfunction sensitizes bladder afferents. eNeuro 4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0381-16.2017. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Liu H, Kuo H (2007) Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistension can reduce nerve growth factor production and control bladder pain in interstitial cystitis. Urology 70: 463-468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.04.038. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chiu B, Tai H, Chung S, Birder LA (2016) Botulinum Toxin A for Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. Toxins (Basel) 8: 201. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070201. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Cockayne DA, Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Rong W, Hamilton SG, et al. (2005) P2X2 knockout mice and P2X2/P2X3 double knockout mice reveal a role for the P2X2 receptor subunit in mediating multiple sensory effects of ATP. J Physiol 567(Pt 2): 621-639. doi: https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2005.088435. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ford AP, Undem BJ (2013) The therapeutic promise of ATP antagonism at P2X3 receptors in respiratory and urological disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 7: 267. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00267. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ito K, Iwami A, Katsura H, Ikeda M (2007) Therapeutic effects of the putative P2X3/P2X2/3 antagonist A-317491 on cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 377: 483-490. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0197-z. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lu SH, Groat WC, Lin AT, Chen KK, Chang LS (2007) Evaluation of purinergic mechanism for the treatment of voiding dysfunction: a study in conscious spinal cord-injured rats. J Chin Med Assoc 70: 439-444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
De Marchi E, Orioli E, Dal Ben D, Adinolfi E (2016) P2X7 Receptor as a Therapeutic Target. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 104: 39-79. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apcsb.2015.11.004. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Gu BJ, Zhang WY, Bendall LJ, Chessell IP, Buell GN, et al. (2000) Expression of P2X(7) purinoceptors on human lymphocytes and monocytes: evidence for nonfunctional P2X(7) receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279: C1189-1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Keay S, Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F, Zhang C, Chai TC, Zhang J (2003) Changes in human bladder epithelial cell gene expression associated with interstitial cystitis or antiproliferative factor treatment. Physiol Genomics 14: 107-115. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00055.2003. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Tseng LH, Chen I, Wang CN, Lin YH, Lloyd LK, et al. (2010) Genome-based expression profiling study of Hunner's ulcer type interstitial cystitis: an array of 40-gene model. Int Urogynecol J 21: 911-918. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-010-1129-x. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Gamper M, Viereck V, Geissbuhler V, Eberhard J, Binder J, et al. (2009) Gene expression profile of bladder tissue of patients with ulcerative interstitial cystitis. BMC Genomics 10: 199. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-10-199. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Dal Susino M, Melchiorri L, et al. (1997) Extracellular ATP triggers IL-1 beta release by activating the purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophages. J Immunol 159: 1451-1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Ferrari D, Wesselborg S, Bauer MK, Schulze-Osthoff K (1997) Extracellular ATP activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through the P2Z purinoreceptor by selectively targeting NF-kappaB p65. J Cell Biol 139: 1635-1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Lee BH, Hwang DM, Palaniyar N, Grinstein S, Philpott DJ, et al. (2012) Activation of P2X(7) receptor by ATP plays an important role in regulating inflammatory responses during acute viral infection. PLoS One 7: e35812. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035812. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Munoz A, Yazdi IK, Tang X, Rivera C, Taghipour N, et al. (2016) Localized inhibition of P2X7R at the spinal cord injury site improves neurogenic bladder dysfunction by decreasing urothelial P2X3R expression in rats. Life Sci 171: 60-67. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.12.017. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Goncalves RG, Gabrich L, Rosario A Jr, Takiya CM, Ferreira ML, et al. (2006) The role of purinergic P2X7 receptors in the inflammation and fibrosis of unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice. Kidney Int 70: 1599-1606. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5001804. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Odobasic D, Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR (2016) Neutrophil-Mediated Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity: The Role of Myeloperoxidase. J Immunol Res 2016: 2349817-11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2349817. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Dell'Antonio G, Quattrini A, Cin ED, Fulgenzi A, Ferrero ME (2002) Relief of inflammatory pain in rats by local use of the selective P2X7 ATP receptor inhibitor, oxidized ATP. Arthritis Rheum 46: 3378-3385. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10678. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Chessell IP, Hatcher JP, Bountra C, Michel AD, Hughes JP, et al. (2005) Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 114: 386-396. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.01.002. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Yan Y, Bai J, Zhou X, Tang J, Jiang C, et al. (2015) P2X7 receptor inhibition protects against ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 308: doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00245.2014. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-
Wan P, Liu X, Xiong Y, Ren Y, Chen J, et al. (2016) Extracellular ATP mediates inflammatory responses in colitis via P2 x 7 receptor signaling. Sci Rep 6: 19108. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19108. [View Article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
-

